What Is a Hash Value and How Does It Work?
Bitcoin is a digital currency that has rapidly gained popularity in recent years. One of the key components of Bitcoin is the hash value, which is a unique identifier associated with each transaction and each Bitcoin block. In this article, we will explore what a hash value is and why it is so important for the Bitcoin blockchain, especially during Bitcoin mining.
What Exactly Does the Hash Value Represent?
A hash value (hash or hash value) is a numerical value used to represent data. It is a unique, fixed-length string of characters created by executing a mathematical function, called a hash function, on a data set.
A hash value is designed to be secure and unreproducible, making it an ideal way to identify and secure Bitcoin transactions and blocks.
When the input data changes, even slightly, the resulting hash value also changes. This allows for detecting changes in the data and transactions, as well as verifying their authenticity.
Indeed, in the case of Bitcoin, the hash is used to confirm the validity of a transaction, ensuring that it has not been changed or corrupted in any way.
What is the Hash Function Used by Bitcoin and How Does it Work?
The Bitcoin network uses the SHA-256 algorithm, which stands for Secure Hash Algorithm 256, to generate hashes for each transaction and block.
This is a cryptographic hash function that takes input of any size and produces a fixed-length output of 256 bits. The output value of the SHA-256 function is usually represented by a 64-character hexadecimal number.
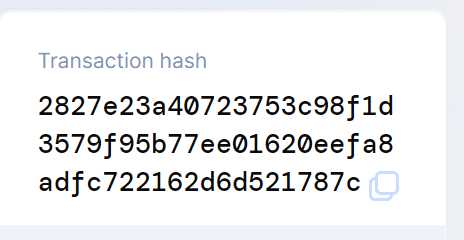
This output is unique for each input and is considered as the digital fingerprint of the input data.
To achieve this result, the SHA-256 function starts by breaking down the input into 512-bit blocks and then subjects it to several series of operations, including XOR, AND, OR, and addition operations. At the end of the process, the 512-bit block is reduced to a 256-bit value.
The SHA-256 algorithm is designed to be secure and resistant to attacks. To do this, it adds additional cycles of operations to the algorithm and ensures that even small changes in the input result in large changes in the output.
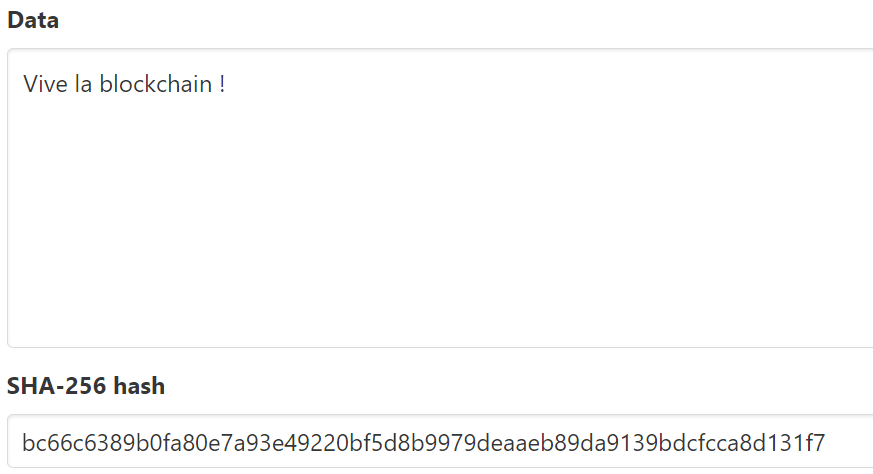
For example, if we encode the phrase “Vive la blockchain!” in SHA-256, we get the following hash value:
“bc66c6389b0fa80e7a93e49220bf5d8b9979deaaeb89da9139bdcfcca8d131f7”.
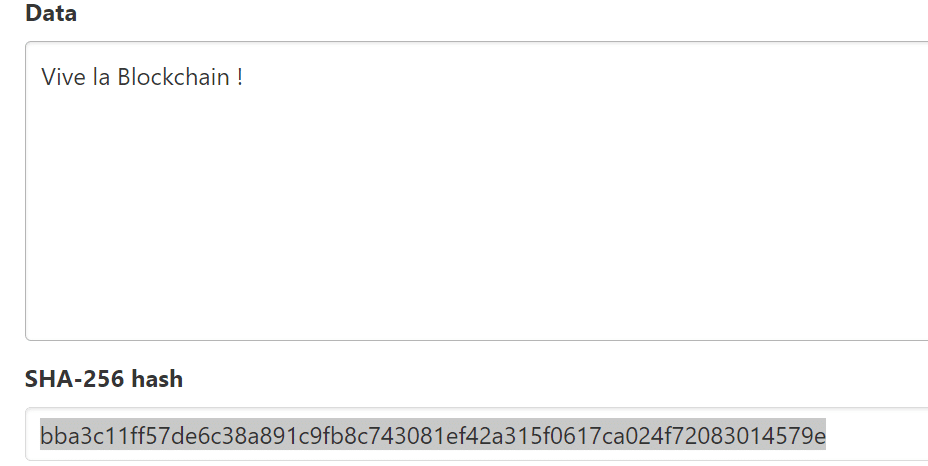
At the same time, if we encrypt the phrase “Vive la Blockchain!” with the same hash function, we get the following hash:
“bba3c11ff57de6c38a891c9fb8c743081ef42a315f0617ca024f72083014579e”. Yet, only the case of the letter “b” changed.
The combination of these characteristics ensures that Bitcoin transactions remain secure.
Why is the Hash Value Important?
The hash value is important for several reasons:
- A hash value serves as an identifier for each individual transaction. This acts as a marker of trust. Each transaction on the Bitcoin network is recorded in the blockchain and has a corresponding hash value. This digital fingerprint allows the transaction to be verified by other users and ensures its legitimacy.
- The hash value also helps maintain the integrity of the Bitcoin network. It is used as a reference point when new blocks are added to the blockchain. Indeed, the hash of a block must match the hashes of the previous blocks for the new block to be accepted as valid. This system helps protect the blockchain, providing an immutable record of all past transactions.
- Hash values are also important when it comes to mining new bitcoins. When miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems, the first miner to find a valid solution for the current block is rewarded with newly issued bitcoins. The miner’s work is verified by comparing the hash value of their solution with the network consensus. If the hash value does not match, the miner’s work is rejected.
- The hash value is also used to generate unique Bitcoin addresses. Each Bitcoin address is associated with a unique hash value, and this hash is used to verify that the address is valid and secure. The calculation of the hash ensures the uniqueness and integrity of the addresses, preventing any malicious alteration. Without the hash value, it would be difficult to differentiate between different Bitcoin addresses, making it easier for hackers to access funds.
What Happens When the Hash Value Changes?
When the hash value of Bitcoin changes, it alerts about the security and integrity of the entire system. Hash values are like fingerprints for digital transactions and provide a unique identifier for each transaction.
If the hash value changes, it means that the transaction is no longer the same and may potentially be fraudulent. Indeed, a new hash value can indicate a change in the underlying data. This could be used to detect double-spending attempts or other forms of fraud.
For example, if a user tries to send two different versions of the same transaction, they will have two different hash values and the blockchain will detect it. The original transaction will be retained, while the new transaction will be automatically rejected by the blockchain.
Conclusion
In summary, the hash value is a key pillar in the functioning of the Bitcoin network. It plays a crucial role in securing the blockchain and provides additional protection to all users. In particular, it prevents the vulnerability of the blockchain to manipulation, fraud, and other malicious activities.
Maximize your Cointribune experience with our "Read to Earn" program! For every article you read, earn points and access exclusive rewards. Sign up now and start earning benefits.
The Cointribune editorial team unites its voices to address topics related to cryptocurrencies, investment, the metaverse, and NFTs, while striving to answer your questions as best as possible.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author, and should not be taken as investment advice. Do your own research before taking any investment decisions.