What Is a Bitcoin Mining Farm?
In the beginning, Bitcoin (BTC) mining was an activity practiced exclusively by a handful of insiders. However, over time, more and more people started to engage in it. As the phenomenon grew, mining farms emerged. In this article, we will look at what these platforms are, how they work, and why they are interesting. We will also see how they are powered, whether they are profitable, and what their future holds.
What is a bitcoin mining farm?
A mining farm is a vast structure that houses equipment for crypto mining. This includes computers (ASIC, FPGA, GPU, CPU) and all other equipment necessary for this activity (computers, routers, etc).
Depending on their goals, these establishments can mine one or more cryptocurrencies. They can therefore decide to dedicate their resources to the BTC network and/or other proof of work (PoW) protocols.
As a reminder, mining is a process that involves deploying computing power to be able to add new blocks to the blockchain. Through this mechanism, the system rewards miners for their efforts by producing new tokens. This encourages some of them to set up large-scale operations to increase their profit margins.
Mining farms occupy a very important place in the crypto industry. This is because they are responsible for producing the majority of the hashrate, which allows the network to be secure and operational.
BTC mining farms vary in size, from small home setups to large commercial enterprises. Generally, it takes several thousand miners (equipment) to qualify as an industrial-scale farm. This type of operation benefits from economies of scale to offer maximum efficiency and yield.
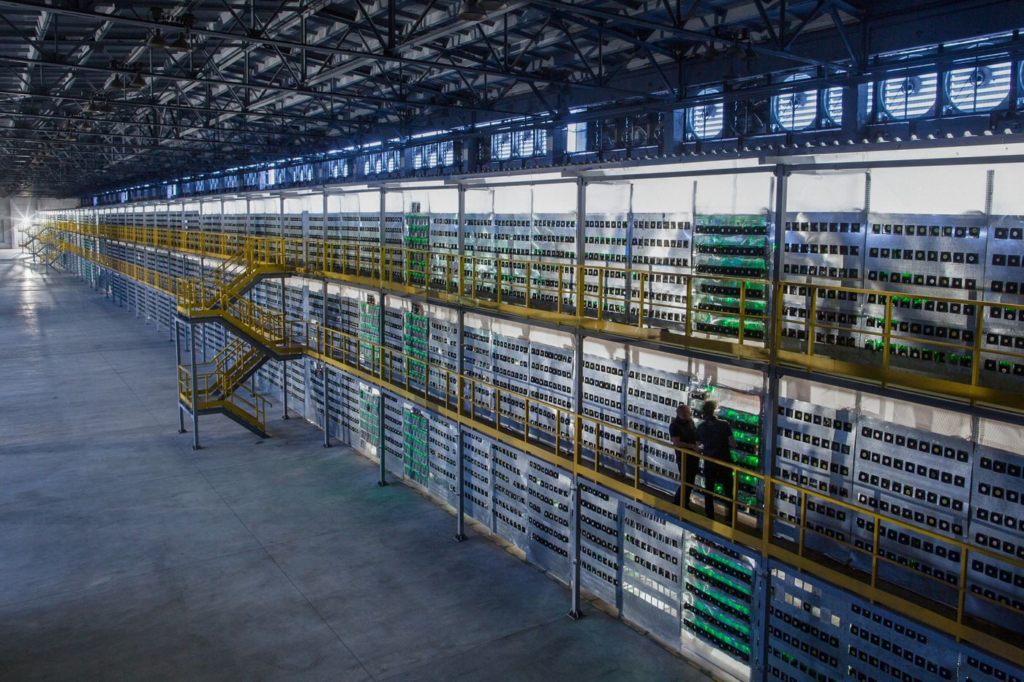

How do mining farms work?
In concrete terms, a mining farm resembles a warehouse where several processing units are stacked on shelves. The resources they produce are pooled together to solve complex mathematical equations.
To ensure greater profitability, the processors must have permanent internet access. Of course, they must also be continuously powered by electricity. Additionally, they must be kept at low temperatures to prevent overheating. This is why mining farms all have a cooling system.
Besides generating a lot of heat, these devices produce a lot of noise, reaching up to 80 decibels. This poses a threat to the ear system. Therefore, the farms are equipped with a sound insulation system.
The mining devices are connected to the blockchain via a mining software, which displays their performance in real time. In addition, a monitoring program allows the remote monitoring of the entire network infrastructure of the farm. It is thus easier to detect, for example, faulty or out-of-service equipment.
The proper functioning of this system requires the presence of qualified technicians on site for maintenance. They are required to ensure the availability of the equipment. Because the fewer functional resources there are, the less likely miners are to be chosen to create new blocks and thus earn rewards.

What is the interest of mining farms?
According to profiles, the motivations that drive people to turn to mining farms are diverse.
From the perspective of farm owners
For them, it is primarily about enhancing their earning opportunities. We should note that the greater an operation’s capacity, the greater the profit prospects.
That said, as large operators, they can achieve substantial savings on maintenance and operating costs (energy, installation, etc.). Moreover, they enjoy certain privileges, especially regarding the price of equipment.
Finally, unlike individual miners, they have easier access to regions where electricity is cheap, knowing that the expenses incurred for their setup are quickly amortized.
From the perspective of small operators
For miners with a modest budget (or startups), it can be interesting to rent the equipment owned by a mining farm (cloud mining). The aim is to exploit them without having to worry about high startup costs or material constraints such as noise, humidity, and overheating.
The farms offer a simpler formula by taking care of installation, insulation, cooling, electrification, configuration, maintenance, etc. Another use of mining farms involves miners who use them to host their own machines.
Where does the electricity consumed by mining farms come from?
To mine Bitcoin, mining farms require a lot of electricity. This is generated from different sources. These range from the heat from thermal power plants to the pressure of water, passing through the mass of air and sunlight. Depending on their geographical location, operations have several options available.
Thermal energy
It is generally produced by burning fossil fuels such as coal, gas, or oil. It is easy to produce and relatively inexpensive. That’s why it is the most common source of electricity in the mining industry. However, thermal energy emits a high level of carbon, contributing to global warming. That’s why miners are increasingly turning to renewable energies.
Hydroelectricity
Hydraulic energy uses the force of water currents to produce electricity. It has the advantage of being more or less regular, as it does not really depend on weather factors. Moreover, its sustainable nature and moderate cost make it an interesting option for BTC mining farms.

Solar energy
It comes from the sun’s rays and is produced by photovoltaic panels. Ideal for domestic or industrial use, it is increasingly popular with cryptocurrency miners.
The sun is a very abundant resource and present all over the world. This makes it a more or less constant source of electricity. This electricity is less expensive than wind. However, its dependence on the sun means that it can only be used reliably at certain times of the day.
Wind energy
This is a form of alternating current electricity produced by wind turbines, taking advantage of the force of the wind. It uses a natural resource available for free 24 hours a day.
Moreover, it does not release greenhouse gases. Each blade offers a much higher energy yield than photovoltaic panels. This makes it a more efficient way to power BTC mining farms while reducing their carbon footprint.
Others
Other more or less common sources of electricity in the mining industry are:
- nuclear, from uranium atom fission;
- geothermal, obtained by extracting heat from the earth’s crust;
- biomass, produced from organic materials.
In which countries to set up a mining farm?
In general, these platforms are set up in regions where electricity is cheaper, temperatures are cooler, and regulations are less restrictive. At the time of writing this article, the most favorable countries are as follows.
The United States
The United States has become the new Eldorado for miners following restrictions imposed by the Chinese government in June 2021. This trend is justified by the fact that the country meets several requirements, among which:
- political and economic stability;
- a regulatory framework favorable to mining in certain states (Texas, Kentucky, Georgia…);
- access to inexpensive electricity supply, moreover from renewable sources (hydroelectricity, wind…).
Russia
This country is rich in natural resources, resources that can be exploited for mining. In fact, the affordable electricity that Russia has is the main asset that makes it one of the most attractive countries for crypto miners.
That said, while mining is widely established in the territory, the taxation associated with this activity is not yet legislated. Another reason for large-scale operations to settle there.
Canada
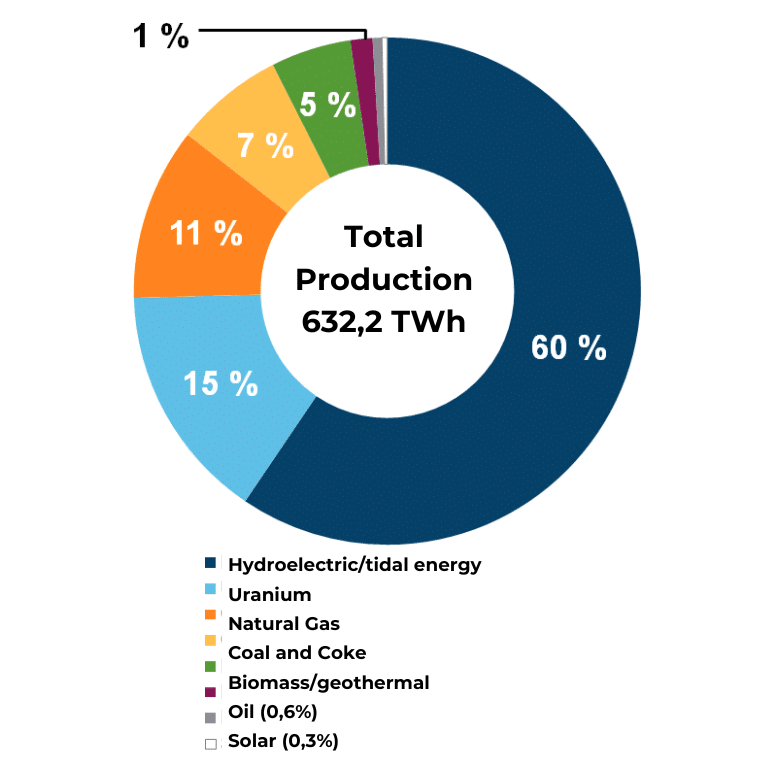
The enthusiasm of miners for Canada is mainly based on the low cost of electricity (only a few cents per kWh). In fact, the country abounds with multiple energy resources. In 2019, nearly 60% of the electricity produced on the territory came from hydroelectric plants. The rest came from renewable sources (wind, biomass, and solar) and natural gas.
Moreover, the country is known for its cool temperatures (an average of 2.1 degrees Celsius). This makes it a perfect place to optimize costs related to cooling a mining farm.
Iceland
In Europe, miners have found a home in Iceland. This is mainly thanks to government incentives and low electricity costs. As a reminder, the energy produced in this country comes from volcanoes (geothermal) and hydroelectric dams. This allows to abundantly benefit from green electricity. This also translates into a decrease in the price of electricity. Crypto mining farms are rushing to seize this opportunity to increase their profits.
Furthermore, the island’s proximity to the North Pole ensures very low ambient temperatures (between 8 and 14.9°C). Enough to effectively cool mining equipment.
Are BTC mining farms profitable?
Companies that mine cryptocurrency make money by operating two main business models. Their main source of revenue consists of mining rewards and transaction fees, when their machines work for their own account.
The second is related to the rental and hosting of mining equipment, depending on whether they own them or not. The billing includes both hosting fees and energy consumption.
For reference, the latter is calculated either according to a contractual rate or based on the season, as is the case with farms using hydroelectricity. Most often, the price during the rainy season is 30% lower than during the dry season.
Factors affecting mining farm profitability
Returning to the initial question, the profitability of bitcoin mining operations depends on several factors such as:
- Electricity cost: in such a setup, electricity is probably the most expensive resource. The more consumption increases, the higher the costs. Miners’ goal is to ensure expenses do not exceed benefits. Therefore, to maximize their profits, farms reduce electricity costs by setting up in areas where this commodity is cheaper;
- Equipment prices: when it comes to mining materials, quality comes at a price. But it is not enough to equip oneself with expensive devices to generate maximum computational power. Other parameters come into play, as well as measures to implement such as: determining the best configuration, choosing an efficient mining pool, etc. Another way to save on hardware costs is to conduct thorough research beforehand to find the devices with the best quality/price ratio. Finally, it’s important to maintain the setup once it has been implemented to use it sustainably;
- The price of bitcoin: knowing that miners are rewarded in BTC, the higher the market value of the crypto, the greater their income.
Recommendations
The construction of a bitcoin mining farm is quite expensive. You must carefully examine these parameters before embarking on such a project.
Consider also that due to Bitcoin halving, the reward per block halves every four years. It is primarily a long-term investment. Therefore, it takes months or even years to hope for profits.
Moreover, monitoring metrics such as hash price will help you optimize your business.

What is the future of bitcoin mining farms?
The last BTC should be mined around 2140. This means that mining farms will no longer receive rewards when they generate new blocks. That said, they can still earn income from transaction fees.
More broadly, the future of farms is closely linked to that of the mining industry as a whole. Depending on the axes, several scenarios are conceivable:
- Regulation: public authorities tend to regulate the sector. Over time, standardization will become a real issue for governments. This approach will certainly result in additional costs for miners: increased taxes and social obligations, stricter requirements for the creation and installation of operations, etc. On the other hand, compliance will contribute to a better control of illegal activities;
- Technology: ASICs currently dominate the market for bitcoin mining. As mining difficulty continues to rise, newer generations of machines (more powerful) could soon emerge to keep mining farms competitive. On the other hand, ASICs are very power-hungry. It is therefore not impossible that FPGAs, which are eco-friendly, will overtake them in the coming years;
- Ecology and electric current: mining farms are increasingly using renewable energy to reduce their environmental impact. This practice is likely to become widespread over time. Besides, farms are likely to deploy new synergies to optimize electricity costs.
In conclusion
Bitcoin farms play a vital role in the development of the ecosystem. In addition to contributing to the proper functioning of the network, they are an excellent way to generate significant profits through mining. That said, before setting up such an installation, miners must absolutely identify and analyze the energy sources available in their region to make an informed choice. By opting for sustainable solutions, they contribute to the advent of more environmentally-friendly mining. Finally, by considering electricity cost, device prices, and the price of bitcoin, miners can increase their profitability prospects.
Maximize your Cointribune experience with our "Read to Earn" program! For every article you read, earn points and access exclusive rewards. Sign up now and start earning benefits.
The Cointribune editorial team unites its voices to address topics related to cryptocurrencies, investment, the metaverse, and NFTs, while striving to answer your questions as best as possible.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author, and should not be taken as investment advice. Do your own research before taking any investment decisions.