Moving Average: Discover This Technical Indicator
In the world of trading, moving averages stand out as leading technical indicators. They allow traders to analyze short-term price fluctuations, providing a clearer view of market dynamics. However, their use requires a deep understanding and judicious interpretation. This article explores the foundations of moving averages, their different types, their limits and pitfalls, as well as practical tips for their use.
What is a moving average?
The moving average is a major technical indicator in trading. It represents the average price of an asset over a specific period, allowing for an understanding of short-term price fluctuations and revealing the general market trend. By analyzing past price data, traders can better anticipate future movements.
The different types of moving averages
Moving averages come in several types, each with its specificities and applications. The simple moving average (SMA) is the most basic. It is calculated by averaging the prices over a set period. Its simplicity makes it a popular choice for identifying the overall trends of the market. However, the SMA assigns equal importance to all values, which can sometimes lead to delays in detecting emerging trends.
The exponential moving average (EMA) is a more sophisticated variant that gives more weight to the most recent data. This feature makes the EMA more responsive to recent price changes, making it ideal for those looking to seize rapid market movements. The EMA is often favored in short-term trading strategies where quick reaction is necessary.
Finally, the linear weighted moving average (LWMA) is another form, assigning increasing weight to the most recent prices. This method offers a balance between the sensitivity of the EMA and the stability of the SMA. The LWMA is particularly useful in volatile markets, as it helps filter out market noise and highlight underlying trends more effectively.
How to interpret moving averages?
Interpreting moving averages is essential for traders seeking to understand market trends. An upward moving average suggests a bullish trend, indicating that prices are rising, while a downward moving average signals a bearish trend, showing that prices are falling. Crossovers of moving averages are also significant: an upward crossover indicates a potential buy signal, and a downward crossover suggests a sell signal. However, it is important to use these indicators alongside other analysis tools to confirm signals and avoid false positives.
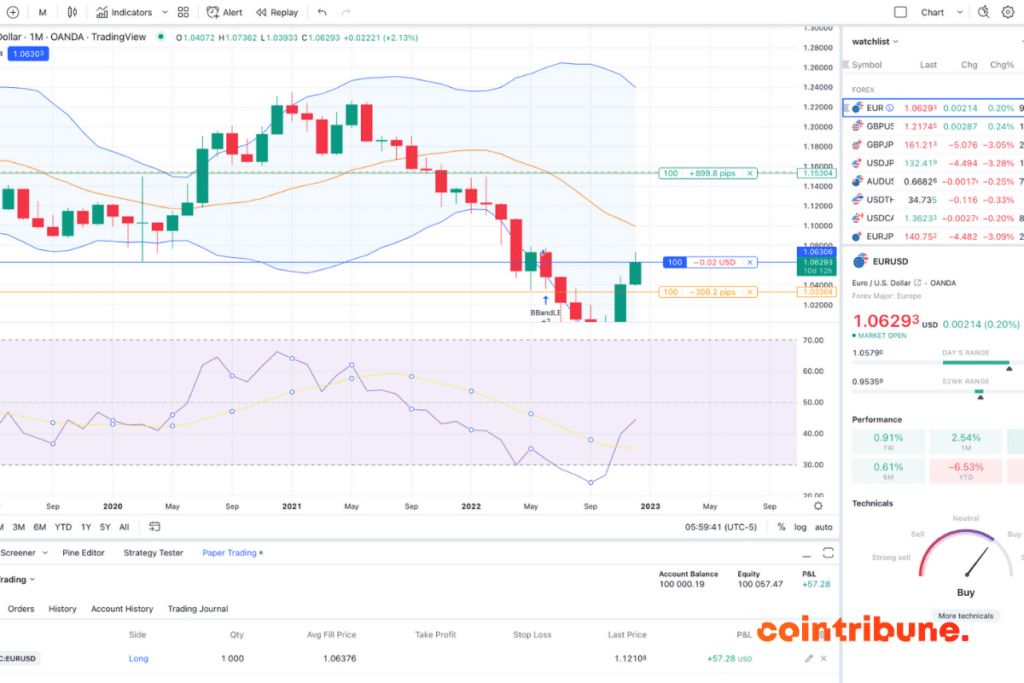
Trading strategies based on moving averages
Moving averages provide traders with a multitude of strategies to navigate financial markets. These strategies, based on the movements and signals of moving averages, allow for the identification of trading opportunities based on trends and price reversal points.
Trend-following strategy
The trend-following strategy involves using moving averages to identify the general direction of the market. Traders observe the current price position relative to a specific moving average. If the price is above the moving average, it indicates a bullish trend, and traders may consider buying positions. Conversely, if the price is below the moving average, it suggests a bearish trend, prompting sell positions. This strategy is particularly effective in markets with clear and prolonged trends. However, it can be less reliable in volatile markets or in the absence of a defined trend, where prices frequently fluctuate around the moving average.
Moving averages crossover strategy
The moving averages crossover strategy is based on observing the crossovers between two moving averages of different periods. A buy signal is generated when the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average, indicating a potential beginning of a bullish trend. Conversely, a sell signal is suggested when the short-term moving average crosses below the long-term moving average, signaling the start of a bearish trend. This strategy is appreciated for its ability to detect trend changes. However, it may also lead to false signals, especially in markets without a clear trend, where moving averages may frequently cross without establishing a reliable trend.
Limits and pitfalls of moving averages
Moving averages, while useful, have inherent limitations due to their nature. Their main disadvantage lies in their reactive character, as they are based on historical data. This reactivity can result in delays in signaling trend changes, especially in volatile markets where price movements are rapid and unpredictable. Traders should therefore be cautious and not rely solely on these indicators for making quick decisions.
Another pitfall of moving averages is the possibility of generating false signals, especially in markets without a clear trend. Under these conditions, prices frequently fluctuate around the moving average, creating signals that may seem to indicate trend changes but are actually normal market variations. This situation can lead to misguided trading decisions, resulting in potential losses.
Practical tips for using moving averages
Effectively using moving averages in trading requires a deep understanding and strategic application. While these indicators are useful, they are not infallible and should be used judiciously. To maximize their effectiveness, it is important to follow practical tips and integrate them wisely into your trading strategy.
Choosing the appropriate period
Selecting the period for the moving average is crucial for its effectiveness. A shorter period will make the moving average more sensitive to price changes, which can be useful for short-term traders looking to capture rapid movements in the market. However, this can also increase the risk of false signals. Conversely, a moving average over a longer period will be less sensitive to short-term price fluctuations, providing a clearer view of the long-term trend. This can be particularly useful for long-term investors or traders looking to avoid short-term market noise. The key is to choose a period that aligns with your trading style and goals.
Combining with other indicators
Moving averages, when used alone, can be limited. To improve their effectiveness, it is advisable to combine them with other technical indicators. For example, using moving averages in conjunction with volume indicators can help confirm the strength of a trend. Similarly, oscillators like the RSI (Relative Strength Index) or the MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) can help identify overbought or oversold points, thus providing complementary trading signals. This multi-indicator approach allows for a more comprehensive market analysis and helps reduce the risk of false signals.
Conclusion
Moving averages prove to be essential tools in the trading world. They provide clear indications of market trends, thus facilitating the detection of opportune moments to enter or exit a position. However, it is important to use them judiciously, recognizing their limits and integrating them into a broader analysis strategy with other indicators like the RSI and Bollinger Bands. By adopting this balanced approach, traders can fully leverage moving averages to refine their trading decisions and improve their performance in financial markets.
Maximize your Cointribune experience with our "Read to Earn" program! For every article you read, earn points and access exclusive rewards. Sign up now and start earning benefits.
The Cointribune editorial team unites its voices to address topics related to cryptocurrencies, investment, the metaverse, and NFTs, while striving to answer your questions as best as possible.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author, and should not be taken as investment advice. Do your own research before taking any investment decisions.