Impact Of The Ecb Pivot: What Are The Consequences?
The ECB made its decision: rates will drop by 25 basis points. A decrease unprecedented in over 5 years. The decision to ease monetary policy by the ECB comes as inflation remains above target, and the United States remains rigid on their monetary policy. The upcoming impacts on financial markets and the value of the euro could be significant if the monetary policy gap between the FED and the ECB becomes persistent. Analysis of the ECB’s decision.

Monetary Policy: The Time for the ECB to Pivot
The ECB’s Governing Council has decided to lower the three key interest rates by 25 basis points. The main refinancing rate will therefore decrease from 4.5% to 4.25%. This decision comes as inflation has decreased by more than 2.5 percentage points since September 2023. However, as the ECB reminds us, inflationary pressures remain strong with wage growth, keeping inflation above target for at least the next year. The new ECB projections for 2024 and 2025 show an increase in general inflation to 2.5% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025, while core inflation would reach 2.8% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025. On the other hand, economic growth is expected to increase to 0.9% in 2024, 1.4% in 2025, and 1.6% in 2026.
“The Governing Council has decided today to lower the three key ECB interest rates by 25 basis points. Based on an updated assessment of the inflation outlook, underlying inflation dynamics, and the strength of monetary policy transmission, it is now appropriate to moderate the degree of monetary policy restriction after nine months of keeping rates unchanged.”
Source: Monetary policy decisions (europa.eu)
As usual, the ECB reminds us that rate decisions will be based on the evolution of the inflation outlook and incoming economic and financial data, as well as the transmission of monetary policy. We will also note that the council will reduce the holdings under the pandemic emergency purchase programme (PEPP) by an average of €7.5 billion per month in the second half of the year.
Towards a New Era of Easing?
Between July 2022 and October 2023, the ECB raised its main refinancing rate from 0% to 4.5%. This is the most restrictive monetary policy in the institution’s history. This restriction appeared more than necessary in view of the rampant inflation, which reached up to 10% in October 2022. Despite the sharp drop in inflation, it seems to persist around 2.5% to 2.6% in 2024. Inflation therefore remains above the ECB’s target of 2%.
The gap to the inflation target is significant if we consider core inflation (inflation excluding raw materials and energy). Core inflation reaches almost 3% in May 2024.Moreover, the 10-year French government bond yield stands at 3%, which is below the ECB’s floor rate but above the inflation target. Despite persistent inflation, it is likely that the ECB takes implicit criteria into account:
- Firstly, the low level of economic growth compared to the United States. This lower growth suggests, although not within the ECB’s mandate, a more accommodative monetary policy.
- Secondly, maintaining rates that are durably higher than inflation can significantly harm the viability of public budgets and a number of companies. It is conceivable that political pressures are exerted in favor of rate cuts. Let’s remember that interest expenses will represent the largest budget for many states in a few years.
François Villeroy de Galhau, the governor of the Bank of France, insists that the ECB has sufficient room for maneuver. In other words, the ECB must significantly lower its key rate. Therefore, pressures to lower rates in the eurozone are persistent, for both implicit economic and political reasons.
“There is now a broad consensus to consider that the risks are balanced. We must avoid two pitfalls, that of rushing, lowering rates too soon, and the pitfall of rigidness, which is acting too late and weighing too much on activity.”
François Villeroy de Galhau – François Villeroy de Galhau considers it “very likely” that the ECB will start lowering its rates “in the spring” (bfmtv.com)
Pivot: The Consequences on the Euro
Monetary policy has a major impact on the value of the currency. Indeed, a decrease in the interest rate, with a fixed foreign interest rate, leads to a devaluation of the local currency. Investors will therefore prefer to invest abroad at a higher rate, leading to capital outflows.
Therefore, the different rates between economic regions indirectly determine the value of the currency. The chart below shows the gap in the key rate between the FED and the ECB, along with the USD/EUR exchange rate. The remuneration of capital between economic regions is one of the major determinants of the currency’s value. Moreover, markets may anticipate the rate movements of central banks. This type of phenomenon can lead to a fall or rise in the exchange rate beyond or below what the rate gap suggests.
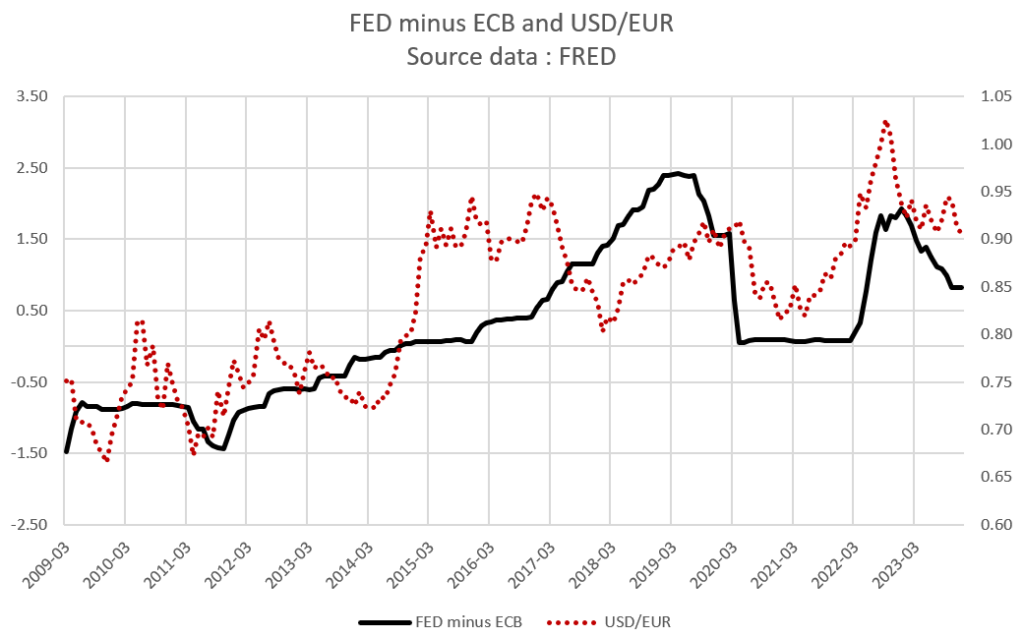
For example, the significant rise of the dollar in 2022 was the result of the ECB lagging behind the FED in reacting to inflation. Therefore, a rate cut by the ECB would be likely to weaken the value of the euro against the dollar.
Lowering Rates Too Much: An Inflation Risk?
Despite everything, the main issue with easing European monetary policy is the potential appearance of a lasting gap with the FED. Indeed, if the American central bank delays lowering its rates, or if the ECB aggressively lowers rates, then a significant rate gap could appear. A rate gap that is too large could harm the euro. Moreover, a significant devaluation of the euro could lead to imported inflation, especially due to the mechanical increase in the cost of imported raw materials.
What Impact on Financial Markets?
Monetary policy is a major issue for financial markets. While financial markets expected a rate cut from the FED in 2024, the robustness of the American economy dashed hopes of a rate cut by summer. The ECB, however, seems to confirm the anticipations. A monetary easing dynamic is thus likely to favor the rise of financial markets.
“Bitcoin has thus become increasingly dependent, although slightly less so than the S&P 500, on the money supply. The money supply thus largely determines the bullish potential of bitcoin. This relationship may clearly question bitcoin’s independence, but a rather lax monetary and fiscal context generally benefits financial assets. ”
Does the money supply influence Bitcoin? – Cointribune
Therefore, the ECB’s rate cut is above all a favorable signal for the economy. Indeed, credit conditions will be eased for the entire economy, promoting greater money creation. The implicit long-term risk is obviously the prospect of observing a new wave of inflation. Moreover, rate cuts could benefit more indebted companies such as small caps. The most speculative or volatile assets would also benefit from a sustained easing of monetary policy.
Nevertheless, rate cuts are not necessarily favorable to financial markets. Indeed, a rate cut with sustained growth resembles a “soft landing.” However, a rate cut can also be a signal of deteriorating economic conditions, which generally leads to a sharp contraction in markets (“hard landing”).
Conclusion
The ECB’s rate cut comes as no surprise to financial markets. The implications of this decision are multiple. Firstly, the ECB is signaling a potentially lasting rate cut while the FED remains inflexible. A lasting rate gap between the different central banks could therefore harm the value of the euro. At the same time, the rate cut comes as growth in the euro zone is almost at a standstill. Moreover, interest expenses weigh heavily on many states and companies.
The ECB’s rate cut is therefore essentially a positive signal for now. However, a significant policy gap with the FED would bring structural risks for the euro. A rate cut does not shield the eurozone economy from an economic slowdown in the next ten months.
Maximize your Cointribune experience with our "Read to Earn" program! For every article you read, earn points and access exclusive rewards. Sign up now and start earning benefits.
Author of various books, financial and economics editor for many websites, I have been forming a true passion for the analysis and study of markets and the economy.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author, and should not be taken as investment advice. Do your own research before taking any investment decisions.