Bitcoin: Transaction Calculations and Confirmations Explained
Bitcoin is a popular cryptocurrency that facilitates secure and decentralized exchanges. Each transfer of bitcoins from one user to another is a mathematically verified operation to ensure the reliability of exchanges. Let’s see how these calculations occur within the network and how they contribute to the Bitcoin mining process.
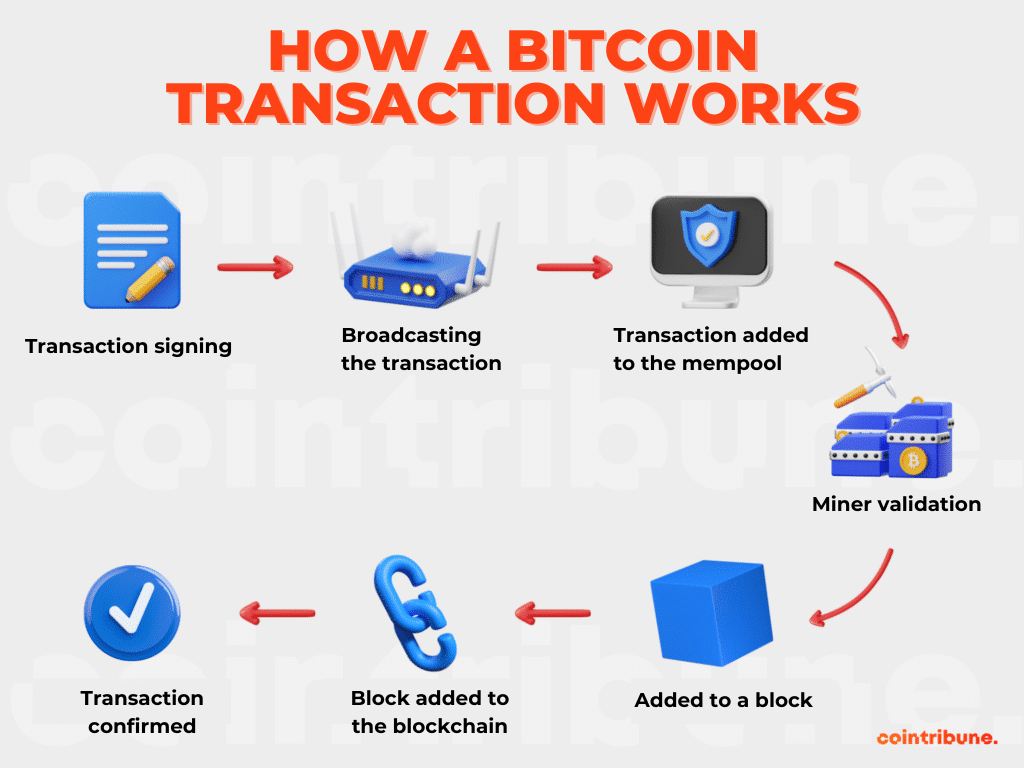
How does a transaction work?
An operation in BTC is the transfer of one or more units (or sub-units) of bitcoins from one user to another. This operation is facilitated by the blockchain, a distributed public ledger that records all exchanges made on the network.
To carry out a bitcoin transaction, the sender initiates a request and digitally signs it using their private key. Then, the details of the operation are broadcasted to the entire network. These details include, among others, their address, the recipient’s address, and the amount to be transferred.
While waiting to be processed, this request is added to the mempool. This is a dedicated storage space for unverified operations. Subsequently, miners verify the validity of this transaction. If it is legitimate, they add it to the next block of the chain.
For a block to be added to the blockchain, the nodes must solve a complex mathematical problem. When a miner finds the solution, a new block is mined, and the transactions included within it are considered final.
What mathematical calculations do BTC miners need to solve?
In reality, they try to find the nonce. Concretely, it’s a number that, when combined with other parameters, including transfer information, timestamp, and the previous block’s hash, allows generating a hash with specific characteristics. The hash calculation, performed using the SHA-256 hash function in Bitcoin’s case, is a crucial step in this process.
As a reminder, the hash is a unique and fixed-length numerical value obtained from input data through a hash function. In Bitcoin’s case, the function used is SHA-256.
In practice, miners generate different nonce values and recalculate the hash with each attempt until they find one that meets the target value conditions.
When a miner finds a satisfying nonce, they submit it to the network for validation. If other miners validate it during the consensus, they will be rewarded with newly created BTC and transaction fees.
How does the network verify the validity of operations?
To verify if an operation is valid, network nodes perform several checks. They first examine the sender’s address in the blockchain to ensure it has the necessary balance. Then, they sum up all the unspent transaction outputs (UTXO) associated with that address.
If the sum of the UTXOs is greater or equal to the amount sent, the transaction is considered valid and is added to the blockchain. If the sum of the UTXOs is less than the amount sent, the operation is considered invalid and is not added to the blockchain.
How is the network fee calculated?
Calculation
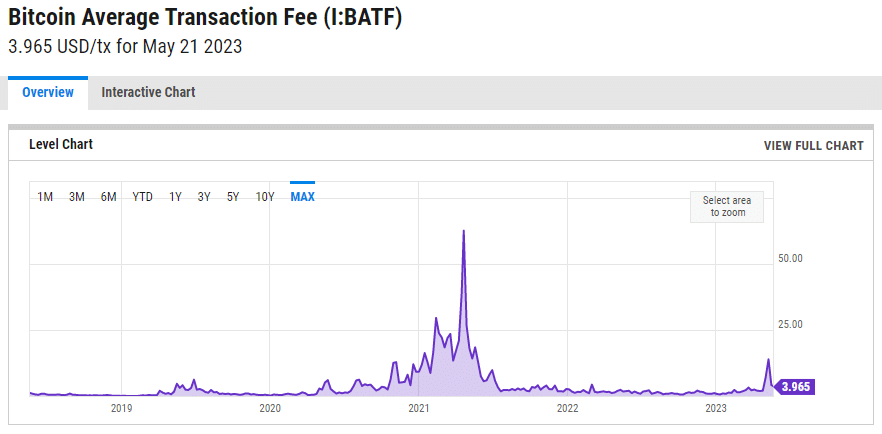
Transaction fees are the payment you make to miners to have your request incorporated into a block. The calculation of these charges is based on two main variables: the transaction size (in bytes) and the current fee rate, usually expressed in satoshis per byte.
The fee rate is set by network miners, while the transaction size depends on the amount of data associated with it.
By multiplying these two factors, we obtain the total amount of fees for each transaction. For example, if your transaction size is 250 bytes and the fee rate is 10 satoshis per byte, the fees will amount to 250 × 10 = 2500 satoshis, or 0.000025 BTC.
Other factors influencing transaction fees
In reality, costs can fluctuate due to a multitude of factors such as:
- High demand: when network activity intensifies, block storage space becomes a more valuable resource. This drives miners to increase the bids;
- Congestion: as requests begin to accumulate in the mempool, miners tend to prioritize those offering higher fees;
- Time: At certain times of the day, the network may be more or less congested, which can affect transaction fees;
- SegWit usage: This update allows reducing the data size per block, which contributes to lowering transaction costs;
- Off-chain transactions: Protocols like the Lightning Network largely reduce network fees;
- BTC value: The higher the value of Bitcoin, the more transaction fees can increase in terms of fiat currency.
Recommendations
When you initiate a transfer, set the fees based on urgency. Transactions with high fees are generally processed as a priority, while those with low fees may experience significant delays.
To optimize processing speed, we recommend paying fees at least equivalent to the median of the last blocks.
How are BTC transactions confirmed?
The confirmation of requests is essential in the functioning of the Bitcoin network. Each operation must be confirmed for funds to be transferred from one party to another.
To do this, it must first be transmitted to the entire Bitcoin network. When miners receive the request, they must use their computers to solve a complex cryptographic puzzle. Once the miner solves the puzzle, the transaction is added to the blockchain and is now considered “confirmed.”
After this process, nodes are rewarded for their efforts with newly created tokens. Once an operation is added to the blockchain, it cannot be canceled or modified. That’s why it’s important for users to ensure they send funds to the correct address and that all details are correct before broadcasting their transaction.
How long does it take to confirm a Bitcoin transaction?
The time required to confirm a bitcoin transaction can vary significantly depending on several factors.
- Cost associated with the transaction: Bitcoin miners prioritize transactions based on the fees associated with them. Thus, higher fees typically lead to shorter confirmation times.
- Transaction size: large operations may require more confirmations than small ones.
- Network congestion: if the network is busy with a large number of requests, confirmation times will be longer.
In general, most transactions are confirmed within 10 to 30 minutes. However, some may take hours or even days, depending on the variables mentioned above. When you send a bitcoin transaction, it is important to understand how long it may take before the funds are available in the recipient’s wallet.
How many confirmations are needed for a bitcoin transaction to be considered final?
A Bitcoin transaction is typically considered finalized once it has been integrated into a block and that block has been added to the blockchain. The number of confirmations a transaction has represents the number of blocks added to the blockchain after the block containing the transaction in question.
Each additional confirmation strengthens the security of the transaction, making it progressively harder for an attacker to alter its details or to double-spend the bitcoins involved.
The number of confirmations required for a transaction to be immutable can vary depending on the context. In practice, three confirmations are sufficient. However, it is recommended to wait for at least six confirmations.
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamentals of the Bitcoin protocol may seem complex, but it is an essential step for any user wishing to appreciate the robustness of this network. The calculations inherent in the mining process ensure the validity of each transaction, while allowing nodes to actively contribute to the network’s operation. Furthermore, confirmations serve to indicate that the transaction has been accepted by the network. The higher the number of confirmations, the more secure the transactions are.
An essential component in the Bitcoin transaction verification process is the calculation of the SHA-256 hash. This cryptographic function transforms transaction data into a unique and fixed digital fingerprint. The robustness of SHA-256, used by Bitcoin, lies in its ability to produce a different hash for every slight modification of input data, thereby ensuring the integrity and security of transactions on the blockchain. Miners, by solving complex cryptographic puzzles, generate these hashes, a process detailed in our article calcul hash sha-256, thereby reinforcing the reliability of the Bitcoin network. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for understanding the security of cryptocurrency exchanges.
Maximize your Cointribune experience with our "Read to Earn" program! For every article you read, earn points and access exclusive rewards. Sign up now and start earning benefits.
The Cointribune editorial team unites its voices to address topics related to cryptocurrencies, investment, the metaverse, and NFTs, while striving to answer your questions as best as possible.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author, and should not be taken as investment advice. Do your own research before taking any investment decisions.