Bitcoin Diamond: History And Functioning Of The Hard Fork
Bitcoin Diamond (BCD) is one of the major blockchain projects that emerged following a hard fork of Bitcoin (BTC). It was designed with the intention of overcoming certain challenges that its predecessor faced. In this article, we will examine the history, operation, and potential advantages of BCD. Finally, we will explore how Bitcoin Diamond might evolve and grow in the future, in an increasingly competitive cryptocurrency market.

Origins of Bitcoin Diamond
To understand the roots of Bitcoin Diamond, it is essential to examine the context in which it was created, as well as the actors and reasons behind its development.
Creation Context
At the time of Bitcoin Diamond’s creation, the Bitcoin blockchain had several shortcomings, such as:
- limited scalability;
- high transaction fees;
- long transaction confirmation times;
- centralization of mining activity.
To address these issues, some developers from the Bitcoin community chose to create a new chain from the main network. This led, on November 24, 2017, to the creation of Bitcoin Diamond at block 495,866 of the original chain.
Date and Initiators of the Project
The hard fork Bitcoin Diamond is the result of the collaboration of two anonymous development teams: Team EVEY and Team 007. The former was the main driving force behind the project and handled most of the development work, while the latter contributed to certain technical aspects and the promotion of the project.
Although the contributors remained anonymous, they regularly communicated via online discussion forums to share their ideas and vision for the project. Their work attracted the attention of many members of the crypto community, thereby contributing to the popularity of BCD.
Motivations Behind the Hard Fork
Essentially, the creation of Bitcoin Diamond aimed to address the limitations of Bitcoin and enhance decentralization. More concretely, it involved:
- increasing the scalability potential of the platform;
- reducing transaction costs;
- accelerating transaction confirmation times;
- ensuring further protection of users’ privacy;
- limiting the dominance of large-scale miners over the network.
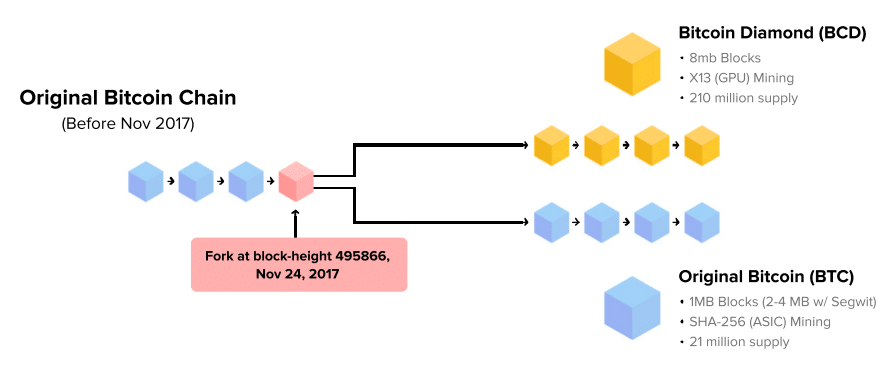
Operation of Bitcoin Diamond
In its operation mode, BCD shares many similarities with the Bitcoin protocol, which is quite normal given that it is a derivative. That said, what interests us more are the notable differences that exist between these two networks, as well as the improvements made to offer a better user experience.
Distribution
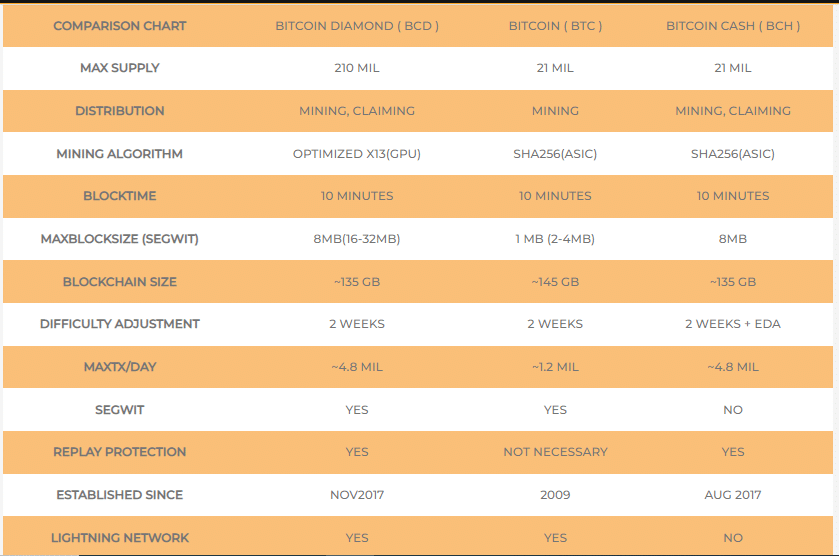
The total supply of Bitcoin Diamond is set at 210 million tokens. This represents ten times the total supply of Bitcoin (21 million).
At the creation of BCD, 170 million tokens were distributed to Bitcoin holders at a ratio of 1 BTC for 10 BCD. The remaining 40 million BCD were reserved to reward miners.
X13 Hash Algorithm
Unlike Bitcoin’s proof of work (PoW) mechanism, which is based on the SHA-256 hash function, Bitcoin Diamond uses X13. This hash algorithm combines 13 different hashing functions and is characterized by its resistance to ASICs (application-specific integrated circuits). This favors mining by graphics cards (GPU).
This feature helps limit the concentration of mining power in the hands of a few dominant players in the industry, ensuring a more balanced distribution of hashrate and improving decentralization.
Increase in Block Size and Integration of the Lightning Network
In the Bitcoin Diamond blockchain, the maximum block size has been increased to 8 MB, while for Bitcoin, it is limited to only 1 MB.
This increase allows for more transactions to be included in each block. This results in a reduction in confirmation times and improves the network’s transaction speed.
Furthermore, a larger block capacity enhances the scalability of the network as it enables processing a greater number of transactions simultaneously.
Additionally, the project integrates the Lightning Network to further reduce costs and optimize transaction processing speeds. By combining this mechanism with SegWit technology (Segregated Witness), which optimizes block storage space, Bitcoin Diamond is capable of achieving up to 100 transactions per second. This corresponds to approximately 4.8 million transactions per day.
Security and Privacy Protection
As Bitcoin Diamond is a hard fork of Bitcoin, it benefits from the inherent security mechanisms of the Bitcoin protocol. This includes the overall computing power of the network and the robustness of its Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithm based on X13, which makes the network more resistant to 51% attacks.
Moreover, transactions on the Bitcoin Diamond network are subject to the same security principles as those of Bitcoin. They are included in the blocks mined by miners, and security is ensured by the PoW consensus.
Regarding user fund security, it largely depends on the wallets used to store and manage their BCD. Indeed, users must opt for reputable, secure wallets and take appropriate measures to protect their private keys.
Additionally, to maintain their privacy, Bitcoin Diamond users can choose to use solutions such as mixing services or wallets compatible with third-party privacy protocols. However, it is important to note that using these services may carry risks.
Utility and Adoption of Bitcoin Diamond
Bitcoin Diamond (BCD) offers multiple advantages to various stakeholders in the ecosystem. Furthermore, thanks to its strategic partnerships and compatibility with several exchanges and crypto wallets, BCD is well-positioned to facilitate its adoption and increase its utility.
Advantages of Bitcoin Diamond
Among the key strengths of Bitcoin Diamond, we can mention:
For Miners
The use of the X13 hash algorithm allows anyone to participate in BCD mining. This creates a more balanced, decentralized, and secure ecosystem.
For Users
Bitcoin Diamond provides faster and cheaper transactions, ensuring an optimal user experience. Additionally, holders of BCD enjoy better conditions regarding privacy.
For Merchants
The adoption of BCD allows merchants to expand their payment methods and reach a young audience within a thriving community. Moreover, the platform is highly secure, and transactions are difficult to trace, which can be considered a major advantage for certain merchants.
Partnerships and Integrations
Thanks to its innovative protocol, BCD has attracted several players in the field who have decided to incorporate it into their services.
Cryptocurrency Exchange Platforms
Among the exchanges that offer BCD are: Binance, OKEx, HitBTC, KuCoin, Bithumb, Huobi, LBank, ProBit, CoinW, and Gate.io.
These platforms allow users to buy, sell, and trade BCD with other cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies, such as the dollar (USD) or the euro (EUR).
Electronic Wallets
Bitcoin Diamond is supported by numerous crypto wallets, providing users with secure and convenient ways to store and manage their tokens.
Wallets compatible with the token include: Bitpie, ZuPago, Atomic Wallet, Paytomat, Lubanso, Ellipal, and ColdLar.
Services and Applications
Many services and applications support BCD. Among them, there are payment gateways and blockchain explorers. In particular, Bitcoin Diamond has already partnered with e-commerce solutions like Chimpion and Shopping Cart Elite to allow merchants to accept BCD as a payment method.
Additionally, through services like BCD Apps, BCD Bazaar, or BCD Pay, Bitcoin Diamond aims to facilitate the use of its currency and encourage its adoption among a broad audience.
Future Perspectives for Bitcoin Diamond
To properly project into the future of Bitcoin Diamond, it is essential to take into account the evolution of its price and market capitalization. But also to be interested in future projects and developments. These elements help to better understand the growth prospects and to adopt an investment or adoption strategy accordingly.
Price Evolution and Market Capitalization
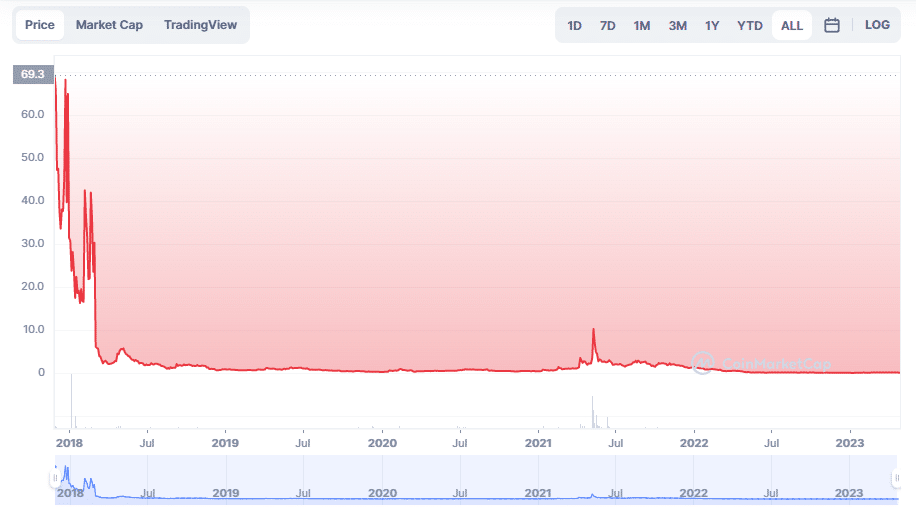
In its early days, Bitcoin Diamond reached a record price of nearly 70 dollars before experiencing a sharp drop to 2.3 dollars. Since then, the BCD has fluctuated around 1 dollar, with some minor and temporary spikes. In May 2021, the token saw a slight increase to reach a new high of 10.31 dollars. However, this upward trend was very brief.
As of the writing of these lines, the token is trading at 0.1762 USD and shows a trading volume of 266,911 USD over the last 24 hours. The circulating supply consists of 186,492,898 BCD tokens with a market capitalization estimated at 32.9 million dollars.
If we consider the historical prices of BCD, we find that market sentiment is relatively stable. This indicates that the token’s volatility is rather low.
Future Projects and Developments
In order to strengthen its position in the cryptocurrency industry, the Bitcoin Diamond development team is actively working to improve the platform’s performance.
Technological Updates
One of its priorities is to enhance the scalability, security, and privacy of its transactions. These developments should contribute to stimulating the long-term adoption of the BCD token.
Expansion of the Ecosystem
Additionally, the project plans to expand its ecosystem by establishing new partnerships. This strategy aims to consolidate the presence of BCD among merchants and users.
Conclusion
Bitcoin Diamond (BCD) promises improvements in decentralization, scalability, costs, transaction speed, and privacy compared to the original Bitcoin. However, its adoption potential is still low, and it faces increasing competition from other hard forks such as Bitcoin Gold, Bitcoin Cash, and Bitcoin SV, which also have attractive value propositions. However, the outcome will depend on technological developments and the ability of each project to convince businesses and investors of their relevance.
Maximize your Cointribune experience with our "Read to Earn" program! For every article you read, earn points and access exclusive rewards. Sign up now and start earning benefits.
The Cointribune editorial team unites its voices to address topics related to cryptocurrencies, investment, the metaverse, and NFTs, while striving to answer your questions as best as possible.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author, and should not be taken as investment advice. Do your own research before taking any investment decisions.